Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) - Object Storage Service
Friday
10 January, 2020
3074 Hits
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) - Object Storage Service
Oracle Technology

Oracle Cloud Infrastructure do provide a high-performance storage platform for a wide range of applications that offers consistent and cost-efficient data robustness. The Object Storage service can store an unlimited amount of unstructured data of any content type, including, backups, analytic data, and rich content, like images and videos.
Knowing that every data stored on storage can be accessed from small websites to the most demanding enterprise application. These files or data stored do have different purposes and can be frequently accessed (hot storage) or less frequently accessed (cold storage).
It is important to know that Oracle offers two types of storage class tier to address the need for both performance, regularly accessed storage, and less regularly accessed storage; Object Storage and Archive Storage.
Oracle Object Storage can be used by organizations or customers for data to which you need fast, immediate and frequent access.
Archive Storage is being used by customers for data to which they rarely access but can be retained and preserved for a long period of time.
To understand Object Storage, let’s look at the three (3) core components:
- Objects: All data, irrespective of the content type of the file, is stored as objects in Oracle Object Storage.
- Bucket: Every object must be stored in a structural way. A bucket is a logical container that can be used to stores objects. With the buckets, all related objects can be grouped together making management and accessibility easy.
- Namespace: A namespace is a logical entity that lets you control a personal bucket namespace. A namespace can contain multiple buckets and each bucket name must be unique within the context of the namespace because it is global. irrespective of the compartment being used to create the bucket, Oracle associates each tenant with a default namespace.
Oracle Object Storage is highly durable and available, and it is uncertain to the data content type and enables a wide variety of use cases. It allows users to automatically replicate objects across multiple fault domains for high durability while actively monitoring data for integrity. With this service, the user can store unlimited objects per bucket for large amounts of unstructured data like videos, backups, and logs. Stored objects can be as small as 0 bytes or as large as 10 TB. Oracle recommends that you use multipart uploads to store objects larger than 100 MB.
Note: Exposing buckets as NFS/SMB mount points on the bare metal compute instances is not supported
Product Features:
- Unified Identity Management
Access to buckets and objects is managed via tight integration with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management.
- Self-Healing
Data integrity is actively monitored using checksums. Corrupt data is automatically detected and healed from redundant copies.
- Encryption
All data stored in the object storage is encrypted at rest, by default, using the AES 256 encryption algorithm.
- Elastic Scaling
Object storage scales elastically and without limits, so there’s no need to estimate your storage requirements upfront.
- Multiple connectivity options
Oracle Object Storage provides a native REST API, along with OpenStack Swift API compatibility, and a Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) plug-in. Oracle Object Storage also currently offers a Java SDK, Console and Python CLI access for management.
It is important to note that users do not need to backup data stored in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage. All objects are stored redundantly on multiple storage servers, across multiple Availability Domains, within a region.
Note: Oracle does not currently use erasure coding in Object Storage. Erasure coding is a way to reduce the capacity required for data redundancy, but it's not required for effective data durability
How do you create an Object Storage Bucket?
Creating a bucket via the console is simple and requires just the name of the bucket, storage tier, and the encryption type.
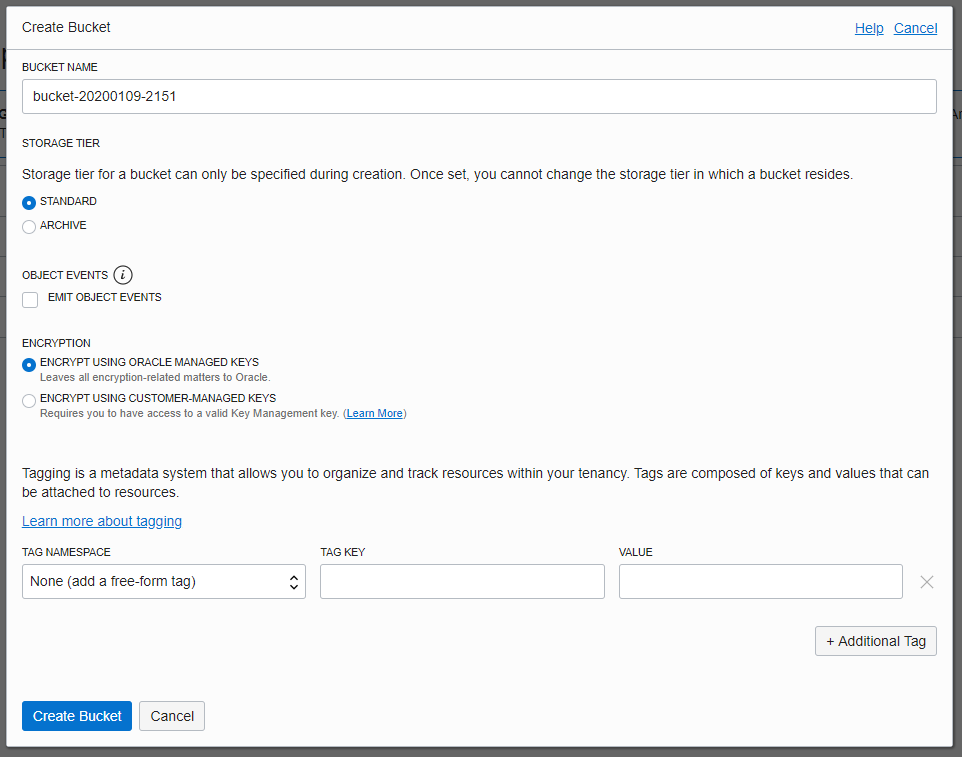
By default, all buckets created on Object storage are private and you will need to edit the visibility property of the bucket to make them public or create a Pre-Authorization request to target the object or the bucket. Pre-authenticated requests offer a mechanism by which you can share data stored in object storage with a third party. PARs eliminates the need to access the object storage data using programmatic interfaces like the API, SDK or the CLI.
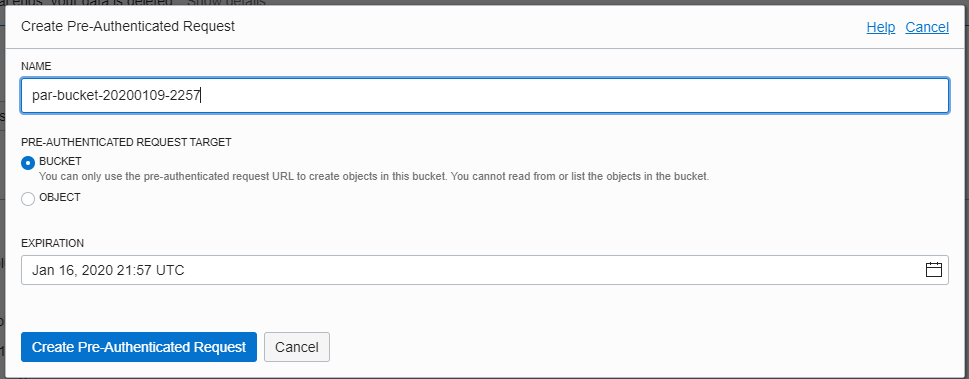
The screen below shows you the console interface that will be used to create PAR.
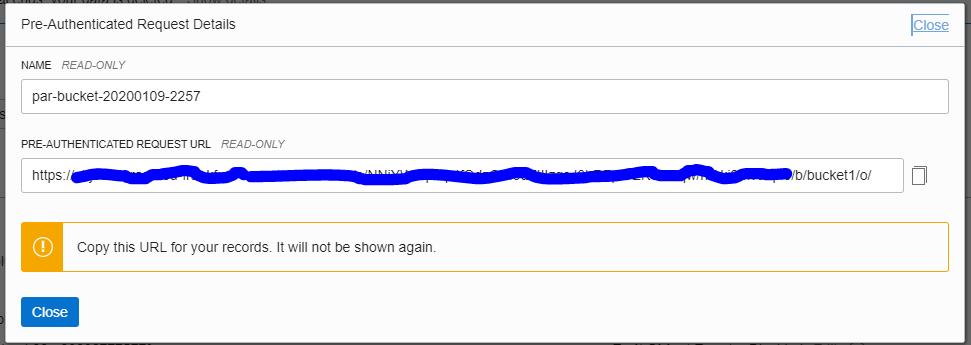
After creating a Pre-Authorization Request, URL generated will be displayed and should be copied before closing.
Looking for the right public cloud storage for the next project or development, you can use the Oracle Object Storage to store and easily access an unlimited amount of data at a low cost.
This blog's content is intended solely for informational purposes. While every effort is made to ensure accuracy, completeness, and relevance, the information may not be current or applicable in all situations. The opinions expressed are solely those of the author and do not reflect the views of any organization they may be affiliated with.