Integrating Tensorflow with Apache Zeppelin
Monday
12 June, 2023
1527 Hits
Integrating Tensorflow with Apache Zeppelin
Technology Trends
Apache Zeppelin is a web-based open-source notebook that allows for interactive data analytics and visualisation. It offers a collaborative environment in which you may develop and execute code in a variety of computer languages such as Python, Scala, R, and SQL.
TensorFlow is a popular open-source library for machine learning and deep learning tasks. It provides a flexible and efficient way to build, train, and deploy various types of machine learning models. In this section, I'll provide you with a brief installation of TensorFlow with Python.
TensorFlow provides many more functionalities for advanced machine learning tasks, such as handling large datasets, distributed training, and deploying models.
To start use Apache Zeppelin, follow these steps:
- Install Apache Zeppelin: Visit the Apache Zeppelin website (https://zeppelin.apache.org/) and download the latest version compatible with your system. Follow the installation instructions provided in the documentation.
- Start Zeppelin: Once installed, start the Zeppelin server by running the appropriate command or script, depending on your operating system. Zeppelin will run as a web application accessible through a web browser.
Note: We assumed you already have Python installed on the system where you wish to run Apache Zeppelin.
TensorFlow must first be installed before it can be used. To install TensorFlow using pip (almost 400MB), use the following command:
pip install tensorflow
this will also check for the availability of numpy on the system, and install if it does not exist.
After the installation, you can create tensors to confirm your installation on a Zeppelin paragraph. Tensors are the fundamental data structures that represent data. You can create tensors using the TensorFlow library in Python.
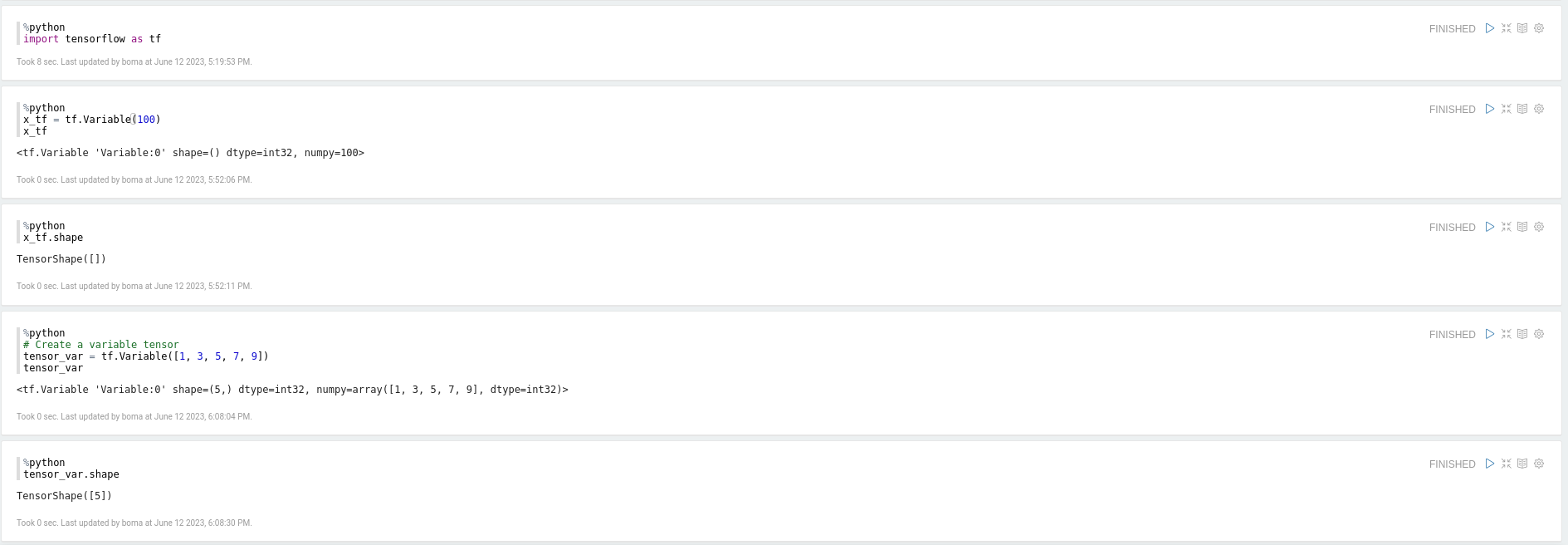
The sample below can be used to test tensorflow using python interpreter.
import tensorflow as tf
# Create a variable tensor
x_tf = tf.Variable(100)
tensor_var = tf.Variable([1, 3, 5, 7, 9])
x_tf
This blog's content is intended solely for informational purposes. While every effort is made to ensure accuracy, completeness, and relevance, the information may not be current or applicable in all situations. The opinions expressed are solely those of the author and do not reflect the views of any organization they may be affiliated with.